"""
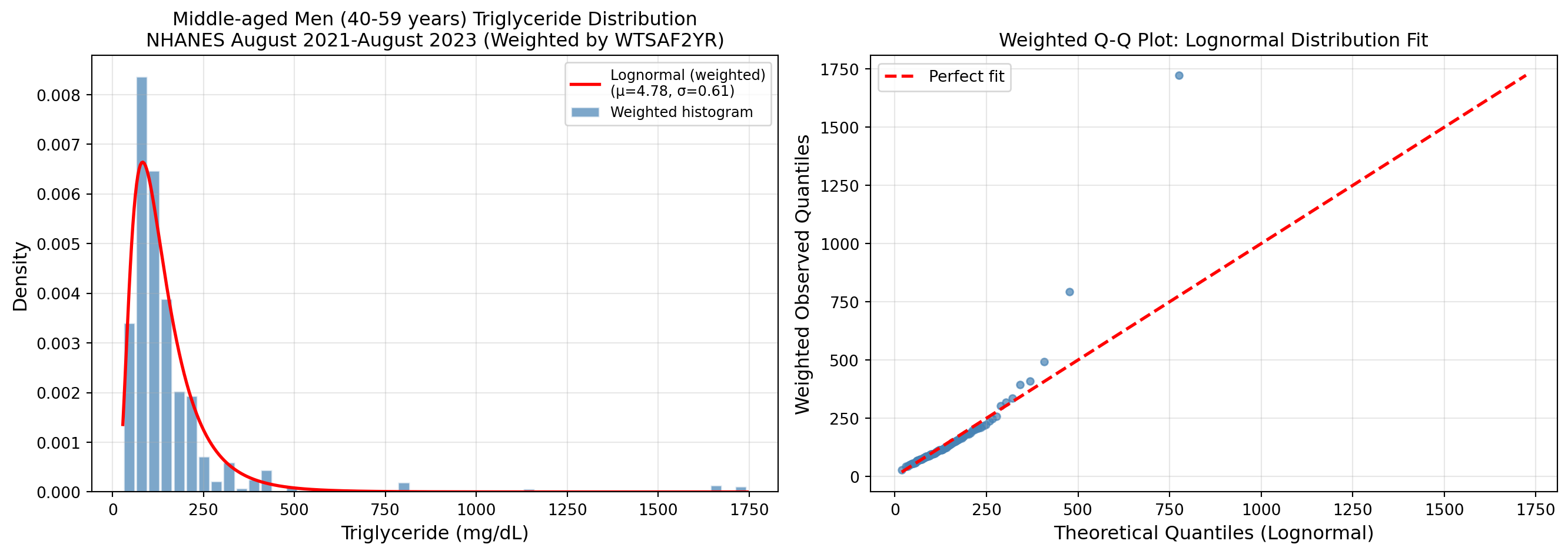
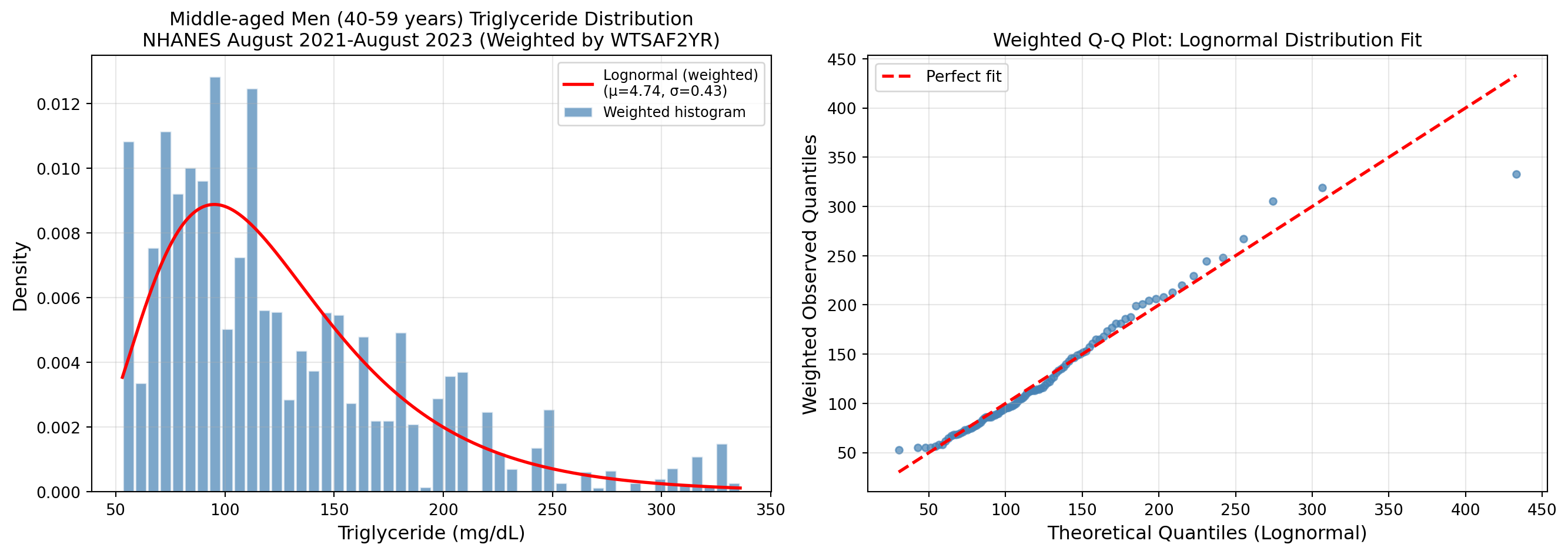
NHANES August 2021-August 2023 中年男性の中性脂肪分析
ヒストグラムとlognormal分布の比較
(サンプルウェイト WTSAF2YR を考慮)
"""
import polars as pl
import pyreadstat
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_data():
"""DEMO_L と TRIGLY_L データを読み込み結合"""
demo_pd, _ = pyreadstat.read_xport("DEMO_L.xpt", encoding="latin1")
trigly_pd, _ = pyreadstat.read_xport("TRIGLY_L.xpt", encoding="latin1")
demo = pl.from_pandas(demo_pd)
trigly = pl.from_pandas(trigly_pd)
df = demo.join(trigly, on="SEQN", how="inner")
return df
def filter_middle_aged_men(df: pl.DataFrame) -> pl.DataFrame:
"""
中年男性(40-59歳)をフィルタリング
- RIAGENDR: 1 = Male
- RIDAGEYR: 年齢
- LBXTLG: 中性脂肪 (mg/dL)
- WTSAF2YR > 0: 有効なサンプルウェイトを持つ参加者のみ
"""
filtered = df.filter(
(pl.col("RIAGENDR") == 1)
& (pl.col("RIDAGEYR") >= 40)
& (pl.col("RIDAGEYR") <= 59)
& (pl.col("LBXTLG").is_not_null())
& (pl.col("WTSAF2YR") > 0)
)
return filtered
def weighted_mean(values: np.ndarray, weights: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""重み付き平均"""
return np.sum(values * weights) / np.sum(weights)
def weighted_std(values: np.ndarray, weights: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""重み付き標準偏差"""
mean = weighted_mean(values, weights)
variance = np.sum(weights * (values - mean) ** 2) / np.sum(weights)
return np.sqrt(variance)
def weighted_median(values: np.ndarray, weights: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""重み付き中央値"""
sorted_indices = np.argsort(values)
sorted_values = values[sorted_indices]
sorted_weights = weights[sorted_indices]
cumsum = np.cumsum(sorted_weights)
cutoff = np.sum(sorted_weights) / 2.0
return sorted_values[np.searchsorted(cumsum, cutoff)]
def weighted_histogram(values: np.ndarray, weights: np.ndarray, bins: int = 50):
"""重み付きヒストグラムのデータを計算"""
hist, bin_edges = np.histogram(values, bins=bins, weights=weights, density=True)
return hist, bin_edges
def weighted_ecdf(values: np.ndarray, weights: np.ndarray) -> tuple:
"""重み付き経験累積分布関数を計算"""
sorted_indices = np.argsort(values)
sorted_values = values[sorted_indices]
sorted_weights = weights[sorted_indices]
cumsum = np.cumsum(sorted_weights)
ecdf = cumsum / cumsum[-1]
return sorted_values, ecdf
def filter_by_percentile(
values: np.ndarray,
weights: np.ndarray,
lower_pct: float = 0.05,
upper_pct: float = 0.95,
) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
重み付きパーセンタイルでデータをフィルタリング
Parameters
----------
values : np.ndarray
観測値
weights : np.ndarray
サンプルウェイト
lower_pct : float
下限パーセンタイル(0-1)
upper_pct : float
上限パーセンタイル(0-1)
Returns
-------
filtered_values : np.ndarray
フィルタリング後の観測値
filtered_weights : np.ndarray
フィルタリング後のウェイト
"""
quantile_bounds = weighted_quantiles(values, weights, np.array([lower_pct, upper_pct]))
lower_bound, upper_bound = quantile_bounds[0], quantile_bounds[1]
mask = (values >= lower_bound) & (values <= upper_bound)
return values[mask], weights[mask], lower_bound, upper_bound
def analyze_and_plot(
triglyceride_values: np.ndarray,
weights: np.ndarray,
save_suffix: str = "",
):
"""ヒストグラムとlognormal分布の比較プロット(重み付き)"""
# --- 重み付きパラメータ推定 ---
log_values = np.log(triglyceride_values)
mu_weighted = weighted_mean(log_values, weights)
sigma_weighted = weighted_std(log_values, weights)
# プロット作成
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
# --- 左: ヒストグラムとlognormal PDF ---
ax1 = axes[0]
# 重み付きヒストグラム
hist, bin_edges = weighted_histogram(triglyceride_values, weights, bins=50)
bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2
bin_width = bin_edges[1] - bin_edges[0]
ax1.bar(
bin_centers,
hist,
width=bin_width * 0.9,
alpha=0.7,
color="steelblue",
edgecolor="white",
label="Weighted histogram",
)
# Lognormal PDF(重み付きパラメータ)
x = np.linspace(triglyceride_values.min(), triglyceride_values.max(), 500)
pdf_weighted = stats.lognorm.pdf(x, s=sigma_weighted, scale=np.exp(mu_weighted))
ax1.plot(
x,
pdf_weighted,
"r-",
linewidth=2,
label=f"Lognormal (weighted)\n(μ={mu_weighted:.2f}, σ={sigma_weighted:.2f})",
)
ax1.set_xlabel("Triglyceride (mg/dL)", fontsize=12)
ax1.set_ylabel("Density", fontsize=12)
ax1.set_title(
"Middle-aged Men (40-59 years) Triglyceride Distribution\n"
"NHANES August 2021-August 2023 (Weighted by WTSAF2YR)",
fontsize=12,
)
ax1.legend(fontsize=9)
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# --- 右: 重み付きQ-Qプロット ---
ax2 = axes[1]
# 重み付き分位点を計算
n_quantiles = 100 # プロット用の分位点数
prob_points = np.linspace(0.001, 0.999, n_quantiles) # 0.1%〜99.9%で裾もカバー
# 重み付き観測分位点
observed_quantiles = weighted_quantiles(triglyceride_values, weights, prob_points)
# 理論分位点(Lognormal)
theoretical_quantiles = stats.lognorm.ppf(
prob_points, s=sigma_weighted, scale=np.exp(mu_weighted)
)
ax2.scatter(
theoretical_quantiles, observed_quantiles, alpha=0.7, s=20, c="steelblue"
)
min_val = min(theoretical_quantiles.min(), observed_quantiles.min())
max_val = max(theoretical_quantiles.max(), observed_quantiles.max())
ax2.plot(
[min_val, max_val], [min_val, max_val], "r--", linewidth=2, label="Perfect fit"
)
ax2.set_xlabel("Theoretical Quantiles (Lognormal)", fontsize=12)
ax2.set_ylabel("Weighted Observed Quantiles", fontsize=12)
ax2.set_title("Weighted Q-Q Plot: Lognormal Distribution Fit", fontsize=12)
ax2.legend(fontsize=10)
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(f"triglyceride_analysis{save_suffix}.png", dpi=150, bbox_inches="tight")
plt.show()
# 統計情報を出力
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("Statistics: Middle-aged Men (40-59 years) Triglyceride")
print("NHANES August 2021-August 2023 (with sample weights)")
print("=" * 70)
print(f"Sample size (n): {len(triglyceride_values)}")
print(f"Sum of weights: {np.sum(weights):,.0f}")
print(f"\n[Descriptive Statistics - WEIGHTED (population estimates)]")
print(f" Mean: {weighted_mean(triglyceride_values, weights):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f" Median: {weighted_median(triglyceride_values, weights):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f" Std Dev: {weighted_std(triglyceride_values, weights):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f"\n[Descriptive Statistics - UNWEIGHTED (sample only)]")
print(f" Mean: {np.mean(triglyceride_values):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f" Median: {np.median(triglyceride_values):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f" Std Dev: {np.std(triglyceride_values, ddof=1):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f" Min: {np.min(triglyceride_values):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f" Max: {np.max(triglyceride_values):.1f} mg/dL")
print(f"\n[Lognormal Parameters - WEIGHTED]")
print(f" μ (log-scale mean): {mu_weighted:.4f}")
print(f" σ (log-scale std): {sigma_weighted:.4f}")
print(f" Median from fit (exp(μ)): {np.exp(mu_weighted):.1f} mg/dL")
# 適合度検定 (Kolmogorov-Smirnov)
def cdf_func(x):
return stats.lognorm.cdf(x, s=sigma_weighted, scale=np.exp(mu_weighted))
# 重み付きKS検定
ks_stat_weighted, ks_pvalue_weighted = weighted_ks_1samp(
triglyceride_values, weights, cdf_func
)
# 有効サンプルサイズ(Kish's effective sample size)
n_eff = (np.sum(weights) ** 2) / np.sum(weights**2)
# 重みなしKS検定(参考)
ks_stat_unweighted, ks_pvalue_unweighted = stats.kstest(
triglyceride_values, cdf_func
)
print("\n[Goodness-of-fit (Kolmogorov-Smirnov)]")
print(" [WEIGHTED]")
print(f" KS statistic: {ks_stat_weighted:.4f}")
print(f" Asymptotic p-value: {ks_pvalue_weighted:.4f}")
print(f" Effective sample size (Kish): {n_eff:.1f}")
print(" Note: p-value uses asymptotic approximation with n_eff")
if ks_pvalue_weighted > 0.05:
print(" -> p > 0.05: No significant difference from lognormal")
else:
print(" -> p < 0.05: Significantly different from lognormal")
print(" [UNWEIGHTED (reference)]")
print(f" KS statistic: {ks_stat_unweighted:.4f}")
print(f" p-value: {ks_pvalue_unweighted:.4f}")
if ks_pvalue_unweighted > 0.05:
print(" -> p > 0.05: No significant difference from lognormal")
else:
print(" -> p < 0.05: Significantly different from lognormal")
print("=" * 70)
def main():
print("Loading NHANES data...")
df = load_data()
print("Filtering middle-aged men (40-59 years) with valid weights...")
middle_aged_men = filter_middle_aged_men(df)
triglyceride_values = middle_aged_men.select("LBXTLG").to_numpy().flatten()
weights = middle_aged_men.select("WTSAF2YR").to_numpy().flatten()
print(f"Sample size: {len(triglyceride_values)}")
print(f"Excluded (WTSAF2YR = 0 or missing): checked")
analyze_and_plot(triglyceride_values, weights)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()